Beginner's guide to git stash command
I will share with examples, how you can benefit from the git stash command
Table of contents
So, What is git stash?
This command is basically used when you want to revert back to the HEAD of the current branch of the repo and store the unsaved changes on the local. Take an example:
Suppose, you are working on the branch 'develop' of your project and modified a few files and created new files. Now, a situation arises that you have to work on some other branch, let's say 'feature-101', of the same project. You cannot switch to the 'feature-101' directly without committing your changes and right now, as you are in the middle of the development, you cannot commit those changes to the 'develop' branch.
Consider another example, where you want to apply the uncommitted changes from 'develop' to 'feature-101' branch, you can use git stash to remove the changes from 'develop' and apply those changes to the 'feature-101usinggit stash apply.
Now, you can only switch from 'develop' to 'feature-101' in the anyone of the following ways:
You commit those changes to the 'develop' branch and checkout 'feature-101'.
You can remove all modified files and delete newly created files from 'develop' and checkout branch 'feature-101'.
Also, you can stash your changes using
git stashand check out the 'feature-101' branch. After completing your work, you can switch back to develop branch and apply those changes back to the develop usinggit stash applycommand.
Useful Stash Commands
Take an example from the screenshot below. You can see the modified files as well as the new files created. Two files marked as U are new unversioned files.
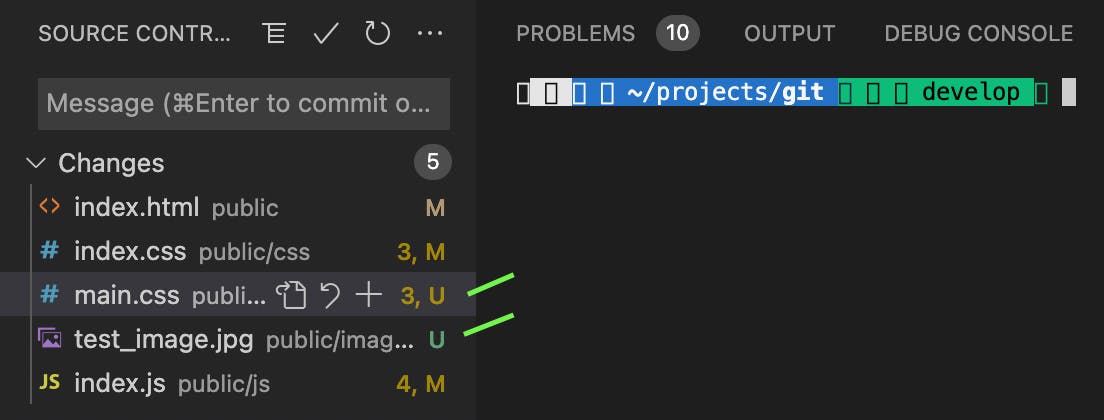
Now, we look into the multiple git stash commands which can be beneficial.
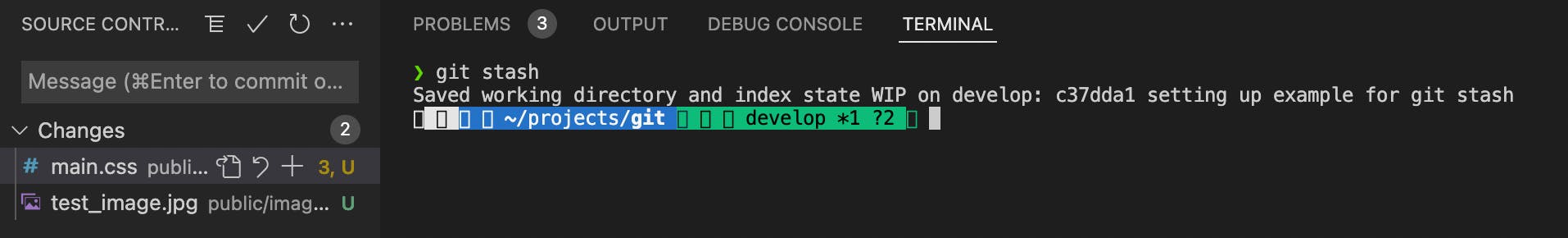
git stashThis command is used to remove the modified files from the current branch of the repo. IMPORTANT This command will not remove the new files created in the current branch. Check below, the modified files have been removed from the current branch. New files are till present.
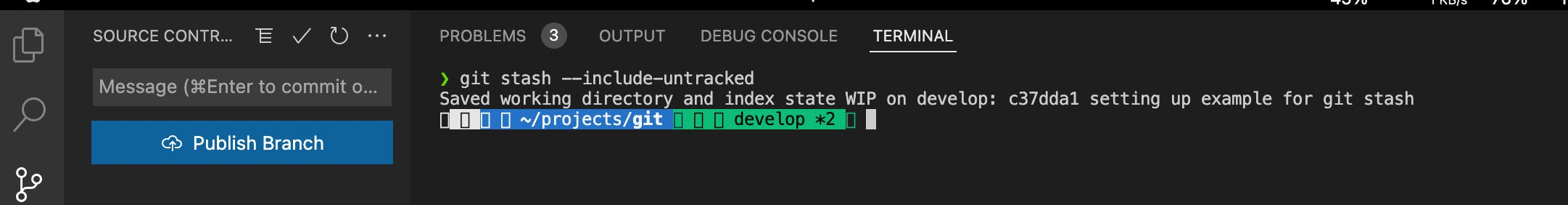
git stash --include-untrackedIf you want to stash the modified files and newly created files from the branch, then you need to usegit stash --include-untracked.
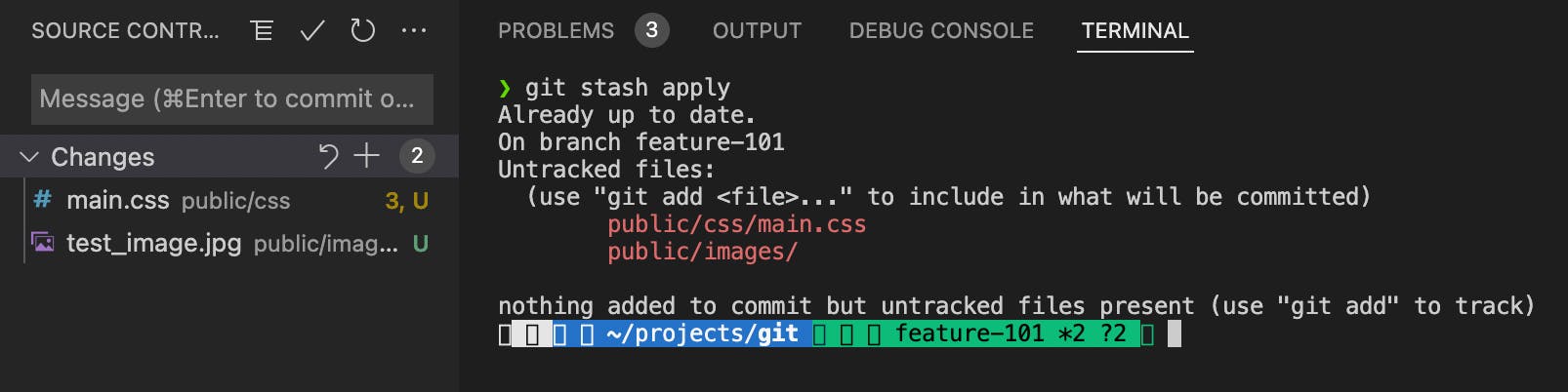
git stash applyThis command will apply the most recent stash to your current branch. Now, I checked out 'feature-101' and enteredgit stash apply
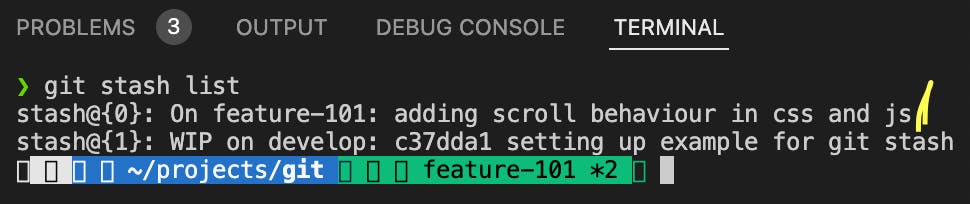
git stash listThis command displays the list of all the stashes present in the local for that repository.
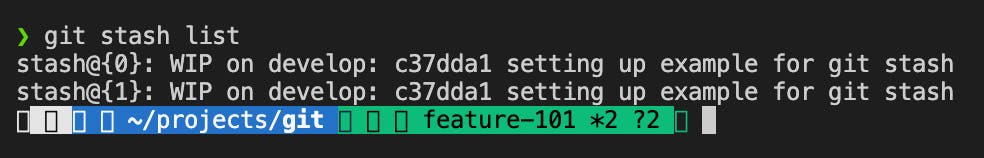
git stash popThis command will apply the most recent stash to your current branch and remove the stash from the local.
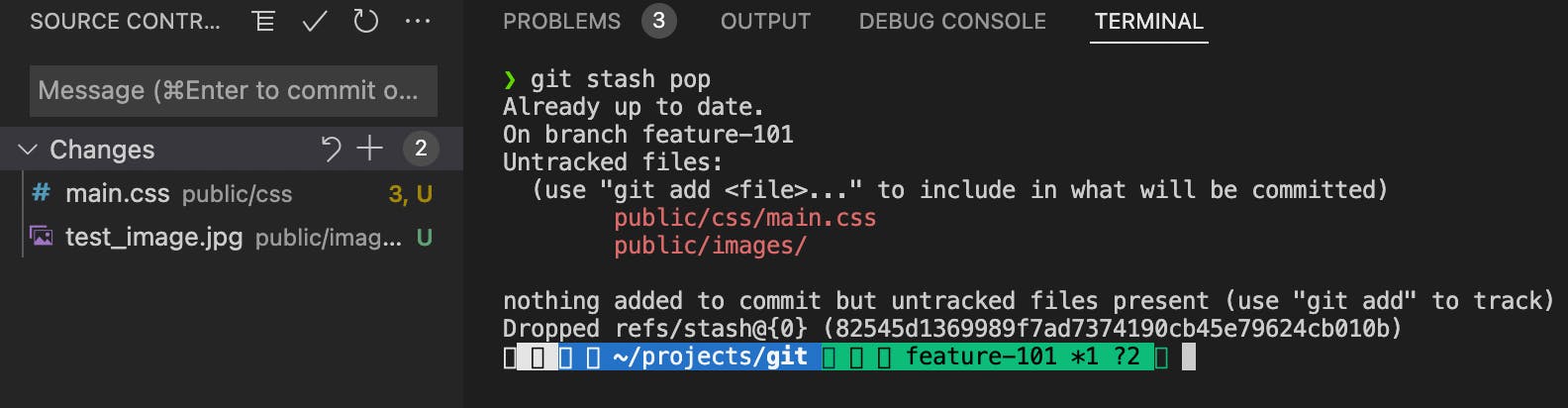
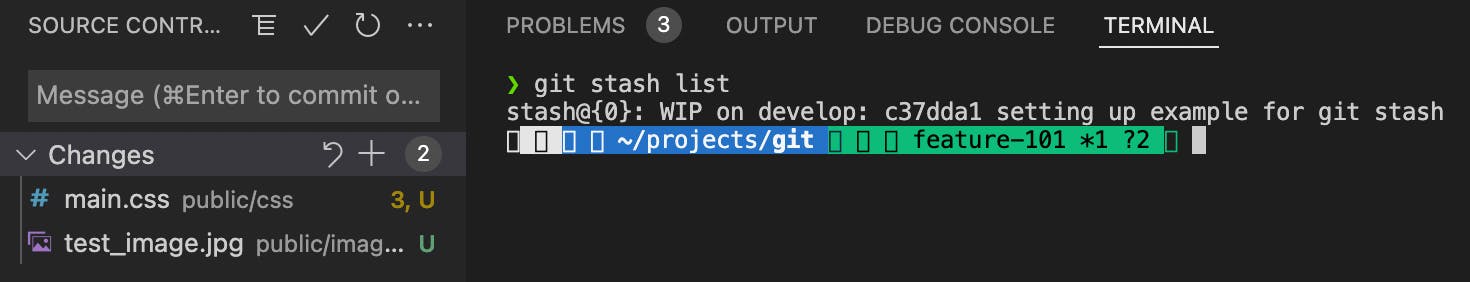
If you check for git stash list, the first stash has been removed from the list.
git stash save <message>One of the most useful commands. While working on a big project, you might have to stash code multiple numbers of time. So, it is a good practice if you store the stash by providing a particularly relevant message so that when you see the stash list, you can easily identify which stash has to be applied.
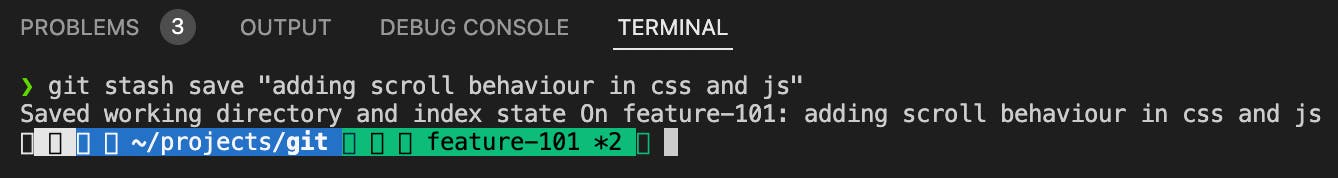
Check the yellow-marked message in the screenshot and match that message with the message in the above screenshot.
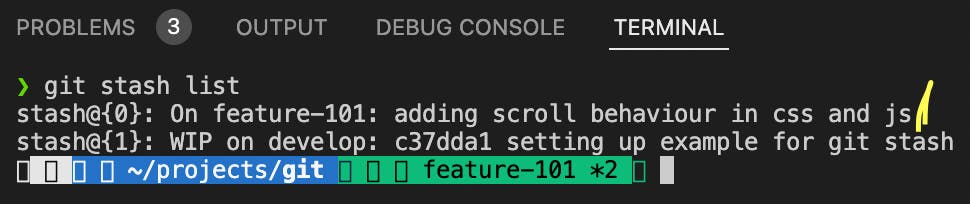
git stash apply stash@{<ver>}After runninggit stash show, you can apply any of the stashes from the stash list by running thegit stash apply stash@{<ver>}and replacing by 0,1,2,3,4,5 depending on the number from the list you want to apply. I will apply the index 1 to the current branch from the stash.
So, git stash is one of the most commonly used commands and will surely help you. These are the most recent commands of the git stash which can make your work easier.
